The Fight Against Anopheles Stephensi
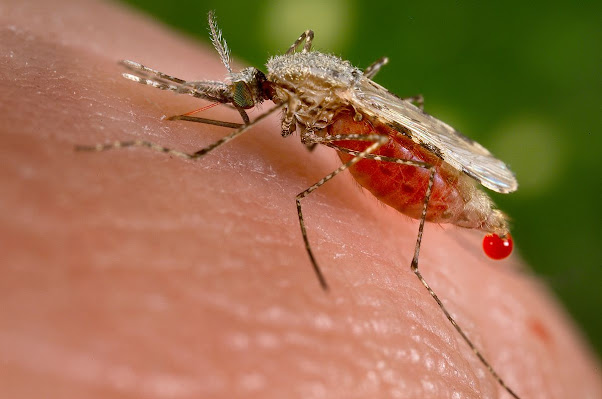
Anopheles stephensi
A species of mosquito that is known to be a vector for the transmission of the Plasmodium parasite, which causes malaria. This species of mosquito is found in the Indian Subcontinent, including India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh, and in parts of Southeast Asia. It is known to be active during the night and is considered one of the most important vectors of malaria in urban areas of India.
The epidemiology of Anopheles stephensi in Africa and Tanzania specifically is affected by a number of factors, including the presence of suitable breeding sites, the availability of human hosts, and the effectiveness of malaria control measures.
In Africa,
Anopheles stephensi is found in a wide range of environments, including urban,
suburban, and rural areas. It is one of the main vectors of malaria in the
region and is responsible for transmitting the disease to a significant
proportion of the population.
This mosquito is particularly well
suited to transmitting malaria in urban
areas because it breeds in artificial
water containers, such as tanks and wells that are commonly found in urban
environments. It is also able to survive in a wide range of temperatures
and humidity levels, making it adaptable to different environments.
Anopheles stephensi is a major
public health concern in India because it is responsible for a large proportion
of malaria cases in the country. Control measures, such as the use of insecticides
and the elimination of mosquito breeding sites, are important for reducing the
transmission of malaria by this species.
Because of the threats that A.
stephensi represents in terms of transmission of malaria, there have been a
number of studies on its behavior, ecology, and response to different control
measures. The goal of this research is to better understand this mosquito
species and develop more effective strategies to control its population and
reduce the transmission of malaria.
Preventing
the transmission of malaria by Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes
involves a number of different control measures.These measures can be divided
into two main categories: environmental management and personal protection.
1.
Environmental
management measures include:
- Eliminating mosquito breeding sites: This includes removing or treating standing water where mosquitoes lay their eggs, such as in tanks, wells, and other artificial containers.
- Using insecticides: This can include the use of insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor residual sprays to kill adult mosquitoes.
- Biological control: This includes using predators, parasites, or pathogens to reduce mosquito populations.
2. Personal protection measures include:
- Using mosquito repellent: This can be applied to the skin or clothing to repel mosquitoes and prevent bites.
- Wearing protective clothing: Long-sleeved shirts, pants, and socks can help to prevent mosquito bites.
- Using bed nets: LLTIN - PBO Insecticide-treated bed nets can provide an additional barrier against mosquitoes and prevent bites while sleeping.
It is important to note that
these measures are most effective when used in combination. For example,
eliminating mosquito breeding sites can reduce the overall mosquito population,
making it less likely for people to be bitten. And when combined with personal
protection measures, such as the use of bed nets and repellent, the risk of
being infected with malaria can be greatly reduced.
Note that: In addition to these control measures, early diagnosis and treatment of malaria cases are crucial in reducing transmission of the disease. This is important because if a person is infected with malaria, they can continue to infect mosquitoes even if they are not showing symptoms, and those mosquitoes can then infect other people.

.png)
Comments
Post a Comment